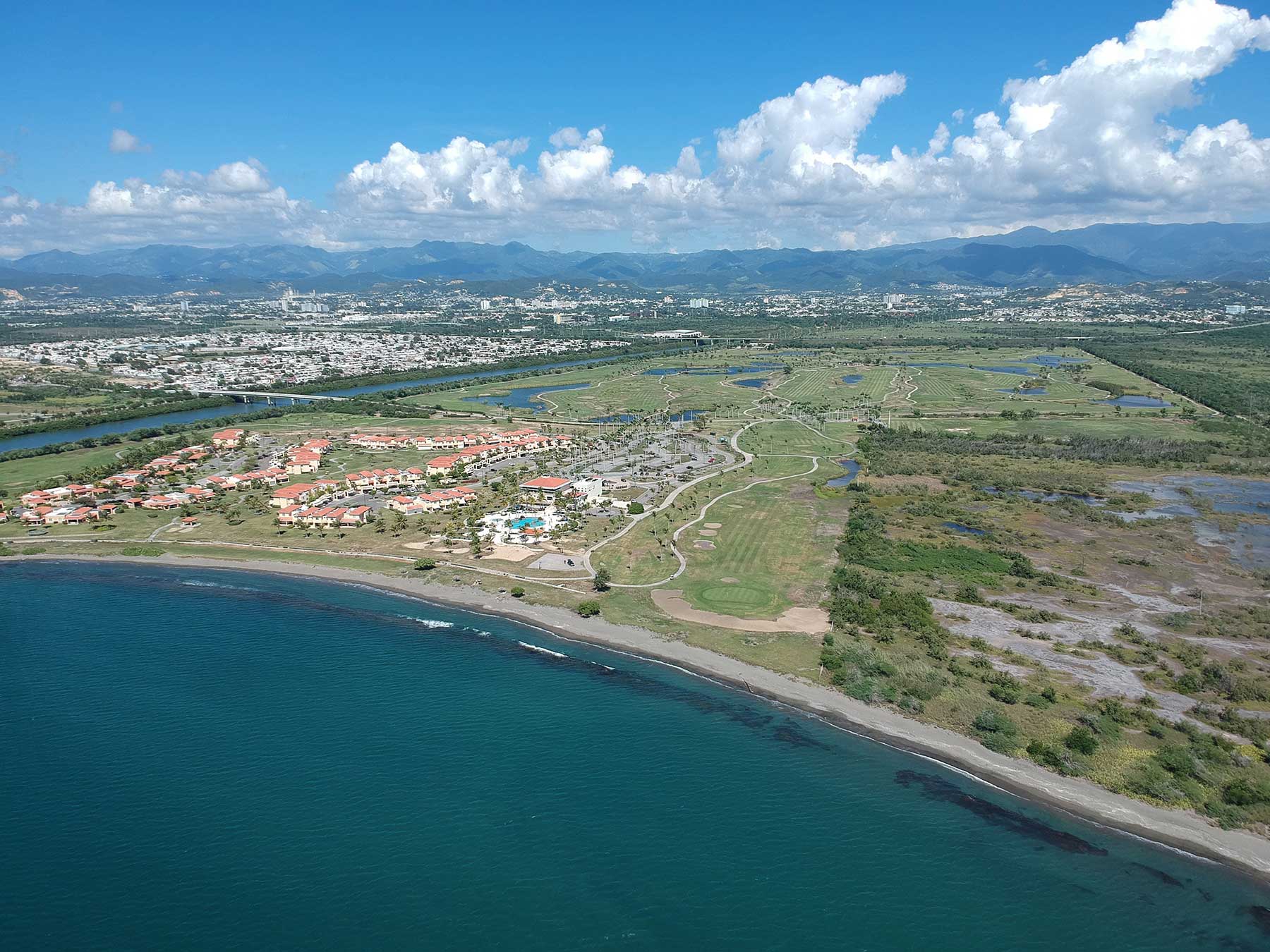
A Beachfront Acre For $30K In An OZ? Welcome To Puerto Rico
Published by Deidra Funcheon, Bisnow Miami
Puerto Rico was already struggling from decades of fiscal mismanagement and had just declared bankruptcy over its $123B debt when it was hit by two hurricanes in September 2017 — only to run into a botched disaster response. The way some see it, though, rock bottom is behind Puerto Rico, and the island is in the early stages of an upswing. “Puerto Rico is setting an incredible pace for economic recovery,” said Brad Dean, CEO of Discover Puerto Rico, a destination marketing organization that promotes the commonwealth. “Airport arrivals are exceeding pre-Hurricane Maria levels, as are lodging revenues. Given the quick rebound, reinvestment in hotel product and tremendous potential for the island’s tourism industry, this is Puerto Rico’s time. From an investor’s perspective, there’s never been a better time to invest in the island’s tourism industry.”
Buildings and infrastructure are still being repaired and upgraded, and the government has instituted a full slate of tax incentives to lure investors, said AG&T Managing Partner Adam Greenfader, who advises clients from his base in Miami. “You can still acquire assets for 50 cents on the dollar,” he said. “Beachfront land in Puerto Rico today can still be acquired at $30K an acre.” Dean and Greenfader will be panelists at Bisnow’s Caribbean Hospitality & Tourism Summit Aug. 1. Puerto Rico’s economic spiral goes back decades. After World War II, it gave big tax breaks to manufacturers, and to cover for revenue shortfalls, issued more bonds than it could repay. In turn, it implemented austerity measures that did little except drive the population away. Its problems were exacerbated by that fact that it has no voting power in Congress.
Greenfader outlined some key developments toward a turnaround. Puerto Rico’s cash-strapped government has tried to lure investors with laws like Acts 20 and 22, passed in 2012 and designed so that people who move to the island pay little or no federal income tax, even on passive investments. Greenfader said this has attracted 250 to 500 families per year, including big names such as billionaire John Paulson. Other incentives include one that lets people with tourism-related projects get back 40% or 50% of their acquisition costs.
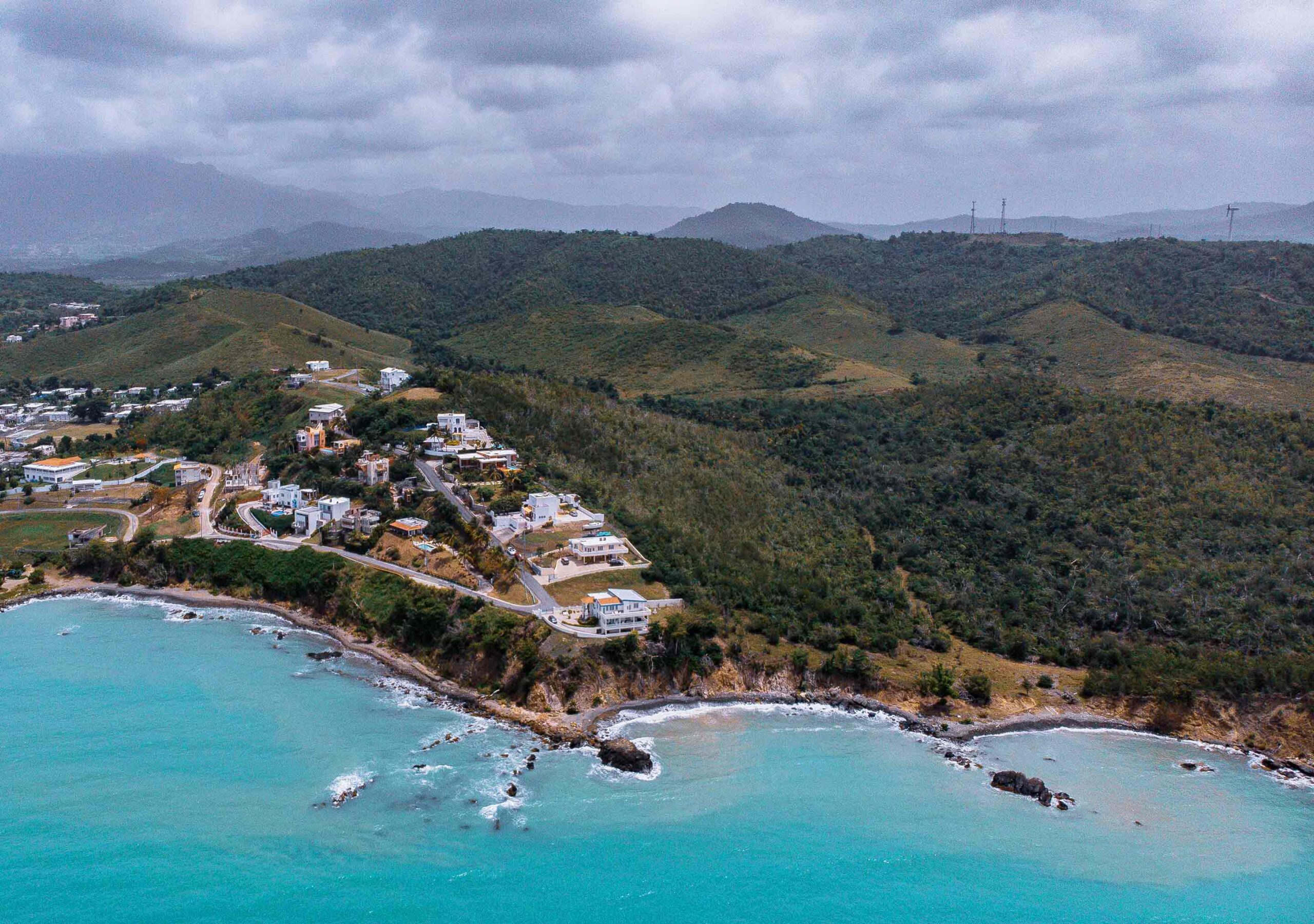

Puerto Rico’s massive government debt is currently being sorted out by a federal oversight board. “The major bonds, COFINA and GO, have been renegotiated and the bondholders have been put into payment plans,” Greenfader said. Since the 2017 hurricanes, federal disaster aid — including $1.4B authorized in June — has trickled in. Hotels damaged in the storms were forced to remodel or rebuild and are now offering better products at higher rates. Many are incorporating solar and microgrids to be resilient for the future. The storms raised the profile of Puerto Rico — one study found that prior to them hitting, about half of Americans hadn’t known the commonwealth was part of the U.S. Airport arrivals and tourism revenue have already set records this year. On top of this, Puerto Rico is the beneficiary of community development block grant funding, and 97% of the entire commonwealth — much of it beachfront — has been designated a qualified opportunity zone. “Puerto Rico never had a 1031 exchange, so from a tax perspective, it’s the first time it’s getting capital gains money,” Greenfader said.
Lifeafar Investments Chief Financial Officer Cole Shephard, who will also be a panelist at the Bisnow event, said his Colombia-based company is already taking advantage of Puerto Rico’s investment climate, raising $16M in an opportunity fund to reposition a 61-room hotel. Shephard said Lifeafar, which started by offering real estate services to expats in Medellín, was drawn by the tax incentives and that the opportunity zone designation was a bonus. He is now doing due diligence on additional properties. “I see the sophisticated money chasing metro San Juan,” he said, suggesting that there is a lot of opportunity for small to mid-market projects outside of the city. Not everything in Puerto Rico is rosy.

As the government has scrambled to generate revenue, sales tax was raised to 11.5%, pensions have been cut, college tuition increased and some 300 public schools closed. Critics have complained that wealthy investors have been protected while ordinary Puerto Ricans suffer. “The locals have had to carry the brunt of these austerity measures,” Greenfader acknowledged. “I’d understand completely, if I see a guy who’s a hedge fund manager with $500M earnings pay hardly any taxes, versus the regular guy paying 35% taxes who’s a salaried worker at Bacardi,” Shepherd said. But Shepherd added that conversations with Puerto Rican officials convinced him they have carefully calculated the tradeoff and found that luring private investment now will help island residents long-term, even though it may take years for the effects to be obvious.
Greenfader suggested that boosting tourism is a winning solution for both investors and residents. Because Puerto Rico since the Kennedy era has been focused on manufacturing, its tourism industry was relatively neglected. The industry now accounts for less than 7% of Puerto Rico’s gross domestic product. In other Caribbean islands, that number is typically between 30% and 80%. Dean’s destination marketing organization, Discover Puerto Rico, was established last year to actively promote tourism. Bisnow’s Aug. 1 Caribbean Hospitality & Tourism Summit will also include Puerto Rico Tourism Co. Executive Director Carla Campos, Hilton VP for Development Juan Corvinos Solans, Puerto Rico Builders Association President Ing. Emilio Colón Zavala and more.